(Provisional Translation)
August 10, 2007
Financial Services Agency
Government of Japan
The Basic Policy and Plan for Financial Inspections in Program Year 2007
The FSA announced today its Basic Policy and Plan for Financial Inspections in Program Year (PY) 2007.
* ''Program year 2007'' refers to the period from July 1 2007 through June 30 2008.
Contact
Financial Service Agency, Government of Japan
Tel +81-(0)3-3506-6000 (main)
Inspection Bureau
(ext. 2514, 2509)
(Provisional Translation)
*This translation is provisionally prepared and subject to change without notice.
August 10, 2007
Financial Services Agency
The Basic Policy and Plan for Financial Inspections in Program Year 2007
I. Basic Policy for Financial Inspections in Program Year (PY) 2007
The Financial Services Agency (FSA) aims to establish a transparent and credible financial regulatory regime while enabling financial and capital markets to provide all kinds of customers with satisfactory financial services, contribute to regional economies and become more attractive to overseas investors. With due consideration to the above objective, the FSA attaches importance to interactive dialogue with financial institutions in its inspections, in line with the Financial Inspection Basic Guidelines, and endeavors to make the revised Financial Inspection Manual and the Financial Inspection Rating System more familiar to financial institutions.
In PY 2007, the FSA will endeavor to conduct inspections in an appropriate and effective manner based on the basic policy explained below while taking account of the ongoing changes in the regulatory environment, such as the implementation of the Financial Instruments and Exchange Law and the New Basel Capital Accord (Basel II), as well as the changes in the financial environment, such as the introduction of more sophisticated and complex financial products and transactions and an expansion of sales channels. Also, the FSA will seek to ensure sound and appropriate management of financial institutions and encourage financial institutions to make best efforts to establish better internal control systems by conducting inspections in an appropriate and effective manner.
1. Basic Concept on Operation of Inspections
(1)To ensure sound and appropriate management of financial institutions, required in the Banking Law and other related regulations, the FSA will adequately conduct its inspections in accordance with the Financial Inspection Manual, which was wholly revised in February this year. Moreover, in conducting its inspections, the FSA will endeavor to examine each financial institution's business management (governance), legal compliance management, customer protection management, and management of all types of risks.
(2)To promote efficient and flexible inspections, the FSA will endeavor to adopt a priority-driven approach for varying the extent of inspections and the number of inspectors deployed based on close examination of the nature of each financial institution's business, characteristics of risks, and financial condition, as well as the effectiveness of its internal auditing.
(3)To encourage financial institutions to make voluntary and sustained efforts toward improvements in their management, the FSA will strive to conduct evaluation appropriately with regard to the Financial Inspection Rating System, scheduled to be put fully into force in January next year.
(4)To enhance the transparency and predictability of the regulation, the FSA will continue to enhance all kinds of measures, exemplified by the release of the FAQ concerning the revised Financial Inspection Manual and a list of examples of issues pointed out in financial inspections. Also, it should be noted that on-site monitoring, which was previously conducted on an ''upon request'' basis, will be applied to all cases in principle as a way to facilitate open communications between the FSA and financial institutions.
(5)To enhance the effectiveness of its inspections, the FSA will maintain close collaboration between the Inspection Bureau and Supervisory Bureau of the agency and also between the agency and the Finance Ministry's Local Finance Bureaus. Moreover, the FSA will endeavor to enhance the inspection capability and expertise of inspectors through professional and practical training and the ''e-learning'' scheme.
2. Priorities in Inspections
With a view of the current situation surrounding financial institutions, the FSA will put priority on the matters mentioned below when conducting its inspections. Especially, amid the ongoing changes in the financial environment, each financial institution is strongly required to set strategic objectives that clarify their company-wide profit targets and strategies for risk-taking, the allocation of human and physical resources, and proactively conduct risk management in line with the strategic objectives and in a manner suited to its characteristics.
Therefore, the management teams of financial institutions are required further enhance the governance system. At the same time, the FSA, when conducting inspections, needs to pay attention to the status of legal compliance as well as the status of proactive efforts to establish the internal control system for each risk category and to put priority on examining whether the business management (governance) system that controls the entire institution is functioning effectively.
(1)Establishment of Risk Management with Due Consideration of Characteristics of Risks and Changes in Financial Environment
Various kinds of lending, such as project finance and financing to investment funds, are increasing while traditional corporate-finance is decreasing. At the same time, various forms of investment management on securities are increasing while the ratios of loan to deposits are still sluggish. Based on these facts caused from changes of financial environment, the FSA will examine the following points in light of the importance of establishing and enhancing appropriate risk management, including a comprehensive risk management, based on analysis and the understanding of the nature and the risk profile of each type of product and transaction.
i)Handling of Various types of Financing
Most financial institutions have improved their risk-taking abilities, so they increase various types of financing, such as project finance, M&A finance, financing to investment funds - especially to real estate funds - and complicated scheme loans through SPC. The characteristics of such new-style financing are of great variety and so complicated, the FSA will examine whether financial institutions have established appropriate screening and risk management systems with due consideration for the nature and characteristics of each type of project and transaction.
In addition, with regard to mortgage loans, the FSA will examine whether financial institutions conduct risk management with due consideration for the composition of their own portfolios and the possibility of interest rate changes.
ii)Development of Appropriate System in response to the Diversification of Investment Products
Most financial institutions are actively investing in increasingly diverse types of investment products such as securitized products including residential mortgage-backed securities (RMBS), structured bonds, fund products and credit derivatives, in addition to investing stocks, government bonds, and corporate bonds.
Since these investment products include various types of risks, investing in such products can have a significant influence on the management of financial institutions with the change of both domestic and international market changes. Therefore, the FSA will examine whether financial institutions establish systems for understanding the nature and the characteristics of the products and transactions used in their investment activities and for accounting and grasping the amount of risk in a suitable manner based on such understanding. In such examination, the FSA will also check the status of the establishment of Asset and Liability Management (ALM).
iii)Appropriate Administration of Outsourcing Business Contractors
In light of an increase in the outsourcing of financial institutions' business operations and diversification of outsourced business operations, the FSA will examine such institutions' systems related to the administration of outsourced business operations, including the system for monitoring such operation, by inspecting outsource contractors as necessary.
(2)Realization of Effective User Protection
The implementation of the Financial Instruments and Exchange Law has strengthened the framework for legal regulation concerning the suitability rule and other elements of user protection, and financial institutions are required to establish more effective user protection management. Given the expansion and diversification of sales channels for financial products, it is also important for financial institutions to ensure that their user protection management functions while handling various operations from product development to after-sale service in sequence. From this viewpoint, the FSA will examine whether financial institutions are making best efforts to establish proactive internal control systems so as to realize effective customer protection, in light of the Checklist for Customer Protection Management of the revised Financial Inspection Manual and the Inspection Manual for Insurance Companies. In conducting its inspections, the FSA will proactively continue to analyze and utilize information collected through the Center for Collecting Inspection-Related Information and the Counseling Office for Financial Services Users.
i)Development of Appropriate System for Fulfilling Liability of Explanation
With due consideration to the increase of sales of risky financial products such as structured deposits, variable annuity insurance products and investment trust products toward general investors, the FSA will examine whether financial institutions establish systems for providing sufficient explanations to customers so as to enable them to engage in transactions based on an understanding of the various risks involved in each financial product. In addition, the FSA will examine whether financial institutions establish systems for preventing transactions in which they abuse their advantageous positions as lenders in ways to undermine the interests of borrowers, with due consideration of the increase in new types of credit provision, such as loan products involving advanced financial engineering techniques and acceptance of privately-placed bonds, whose risks are of a different nature from the risks involved in traditional loans.
Also, the FSA will examine the appropriateness of financial institutions' disclosure, since the enhancement of disclosure of financial institutions' risk information is beneficial for customers from the viewpoint of market discipline and the foundation of user protection.
ii)Handling Consultation Requests and Complaints from Customers
In light of the fact that financial institutions' responses to consultation requests and complaints from customers are still insufficient in many cases, the FSA will examine the appropriateness of financial institutions' responses to such requests and complaints, for example, by examining whether their handling of customers and reporting to the management are done in a timely and appropriate manner and whether they sufficiently analyze the causes and reasons for consultation requests and complaints and consider and implement measures for preventing the recurrence of problems promptly and appropriately.
iii)Efforts to Ensure Safety of Financial Transactions
In light of the high incidence of crimes related to ATM systems and the occurrence of financial crimes related to Internet banking in recent years, the FSA will examine the status of financial institutions' establishment of systems for enhancing information security measures to prevent financial crimes through illegal use of ATM systems and Internet banking in a manner suited to the nature and direction of their own businesses.
(3)Appropriate Response to Globalization of Financial Transactions
i)Handling of Financial Conglomerates and Internationalization
In response to the development of financial conglomerates, the FSA will examine conglomerates' comprehensive risk management on a group basis in cooperation with the Securities and Exchange Surveillance Commission as necessary. Moreover, in light of increasingly active overseas business operations, the FSA will examine the appropriateness of administration of overseas branches by divisions in charge of supervising international business operations. In such examination, the FSA will further strengthen its collaboration with overseas authorities, particularly those in Asia.
ii)Appropriateness of Anti-Money Laundering Efforts
Considering the fact that making thorough efforts in anti-money laundering has become a critical challenge all over the world, the FSA will examine the status of financial institutions' establishment of systems for dealing with money laundering at their domestic branches and the management of anti-money laundering efforts at overseas branches by their divisions in charge of supervising international business operations. The FSA will also examine whether financial institutions take appropriate measures to deal with the changes in the regulatory environment, such as an expansion of the range of services for which customer identity verification is necessary and the establishment of the Law for Prevention of Transfer of Criminal Proceeds.
(4)Response to Structural Changes Related to Regional Finance
Amid drastic structural changes related to regional finance, the FSA will examine whether regional financial institutions establish appropriate risk management in response to changes in the environments surrounding them, with due consideration of the growing importance of the role played by such institutions in the revitalization of regional economies and the renovation of regions.
i)Involvement in Business Revitalization of Small- and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) and Regions
Active involvement of regional financial institutions in locally-oriented finance projects such as the business rehabilitation of SMEs is essential for the renovation of regions. Therefore, the FSA will evaluate and examine, in accordance with ''The Supplementary Book to the Financial Inspection Manual: Treatment of Classifications regarding Credit to Small- and Medium-Sized Enterprises,'' whether such institutions are making further voluntary and sustained efforts to establish appropriate credit risk management, for example, by developing close relationships with SMEs.
ii)Efforts not to Rely Heavily on Real Estate Collateral and Personal Guaranty in lending
Considering the fact that, in promoting regional finance, it is important to make full use of a financing scheme focusing on project value without placing undue emphasis on real estate collateral or personal guaranty, the FSA will examine the efforts of each financial institution based on the revised Financial Inspection Manual that made clear the treatment of personal property and loans as collateral.
3. Priorities in Specific Financial Sectors
In addition to the above-mentioned general inspection priorities, the FSA will put priority on the matters explained below with regard to specific financial sectors in ways to aptly reflect institutional reforms such as the implementation of the Financial Instruments and Exchange Law and the amendments of the Trust Business Law and the Money Lending Business Control and Regulation Law as well as the privatization of Japan Post.
(1)Deposit-Taking Financial Institutions
With regard to deposit-taking financial institutions, the FSA will examine the status of their efforts concerning user protection, including those to fulfill their liability of explanation to customers. Moreover, the FSA will conduct inspections in a manner suited to the scale and characteristics of individual financial institutions; the FSA will examine financial institutions' credit risk management, including the status of large lending management as well as their market risk management in light of their respective financial conditions and asset management status.
Another noteworthy point is that in accordance with the implementation of Basel II, the FSA will examine whether they develop the proactive risk management by examining the appropriateness of their internal rating system on credit risk. Also, the FSA will examine whether they develop administration so as to appropriately conduct international operations and management to prevent conflicts of interest that is suitable to the diversification of their businesses.
With regard to bank agents, the FSA will conduct inspections as necessary considering the status of the entry into the bank agency businesses.
(2)Trust Banks
The product range of the trust business has been diversifying, as shown by an increase in the volume of small-lot products for individual investors and products for the wealthy class. Considering this background, the FSA will examine the responsibility of explanation of trust banks' to customers, in order to enable customers to carry on transactions based on an understanding of the various risks involved in such products. Moreover, the FSA will examine their management for screening entrusted assets as well as the management for ensuring appropriate asset management through measures such as the prevention of conflicts of interest, in accordance with the Inspection Manual for Trust and Banking Companies.
(3)Insurance Companies
With regard to insurance companies, the FSA will examine the insurance sales management system, including the management of insurance agents such as banks. For example, the FSA will examine whether insurance companies and their agents conduct their soliciting activity by fulfilling their responsibility of explanation about products or based on the needs of customers. The FSA will continue to examine the management for payment of insurance claims. Moreover, the FSA will examine their management for separate accounting and for policy reserves in a manner suited to their underwriting risks and the characteristics of their products. Also the FSA will examine is the appropriateness of their risk management related to the diversified investment vehicles such as fund investing.
(4)Foreign Financial Institutions
With regard to foreign financial institutions, the FSA will examine their compliance with Japanese laws and regulations, with taking account of the above-mentioned sector-by-sector inspection priorities. Also, the FSA will examine whether they establish effective business management in light of the scale, characteristics and their groups expansions. Moreover, the FSA will examine whether their private banking business and sales of financial products involving derivatives are conducted under appropriate management from the viewpoint of user protection.
(5)Consumer Finance Companies and others
With regard to consumer finance companies, the FSA will examine the status of their compliance with the various regulations on their activities in accordance with the existing Money Lending Law and related regulations (e.g., the ban on excessive lending, the regulation on collection activities, and the ceiling on interest rates). After the implementation of the revised Money Lending Business Control and Regulation Law, the FSA will also examine the status of their compliance with that law.
With regard to issuers of prepaid cards, gift coupons and others, the FSA will examine the status of their depositing of issuance security deposits.
(6)Government-Affiliated Financial Institutions
With regard to government-affiliated financial institutions, while paying attention to the progress of the reform of the policy-based financial system, the FSA will conduct inspections in accordance with the revised Financial Inspection Manual that is applied to the inspection of private financial institutions with giving a consideration to the nature of each institution.
(End)
II. Basic Plan for Financial Inspections for PY2007
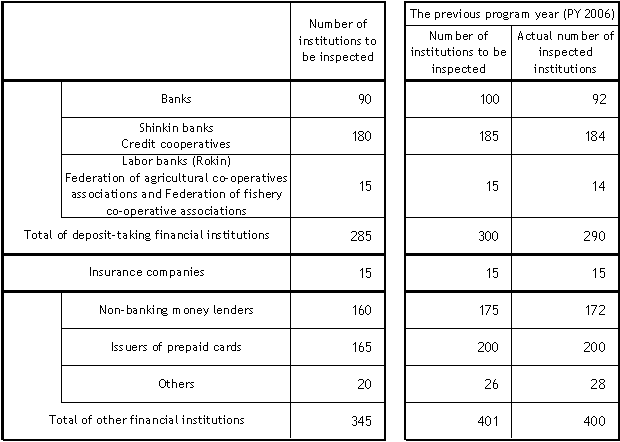
Note:
(1) These inspection numbers may be changed as necessary.
(2) Figures on the ''Banks'' are the aggregated numbers of inspected banks and inspected bank holding companies. Those of ''Insurance companies'' are also the aggregated numbers of inspected insurance companies and inspected insurance holding companies.
Site Map
- Press Releases & Public RelationsPage list Open
- Press Releases
- Press Conferences
- Official Statements
- FSA Weekly Review & ACCESS FSA
- Speeches
- For Financial Users
- Others
- Archives
- Laws & RegulationsPage list Open
- Name of Laws and Regulations(PDF)
- Recent Changes (Legislation, Ordinances, Guidelines)
- Guidelines
- Financial Instruments and Exchange Act
- Financial Monitoring Policy
- Public Comment
- No-Action Letter System
- Procedures concerning Foreign Account Management Institutions